Gastroshiza is a rare and complex congenital condition that impacts newborns, causing significant concerns for parents and healthcare providers alike. Though it is relatively uncommon, the severity of gastroshiza cannot be underestimated, as it often presents with serious complications that require immediate medical intervention. This article provides an in-depth look into gastroshiza, explaining its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and the long-term outlook for affected children. By exploring this topic from multiple perspectives, we aim to offer insights that surpass the quality of existing online sources, ensuring this content is both informative and optimized for search engine results.
What is Gastroshiza?
Gastroshiza is a birth defect in which a baby is born with the intestines protruding outside the body through a hole in the abdominal wall. This condition occurs during fetal development when the abdominal muscles do not fully close, leaving an opening through which the intestines push out into the amniotic sac. Unlike omphalocele, another condition that also causes the intestines to be outside the body, gastroshiza typically does not involve other organs and tends to affect only the intestines.
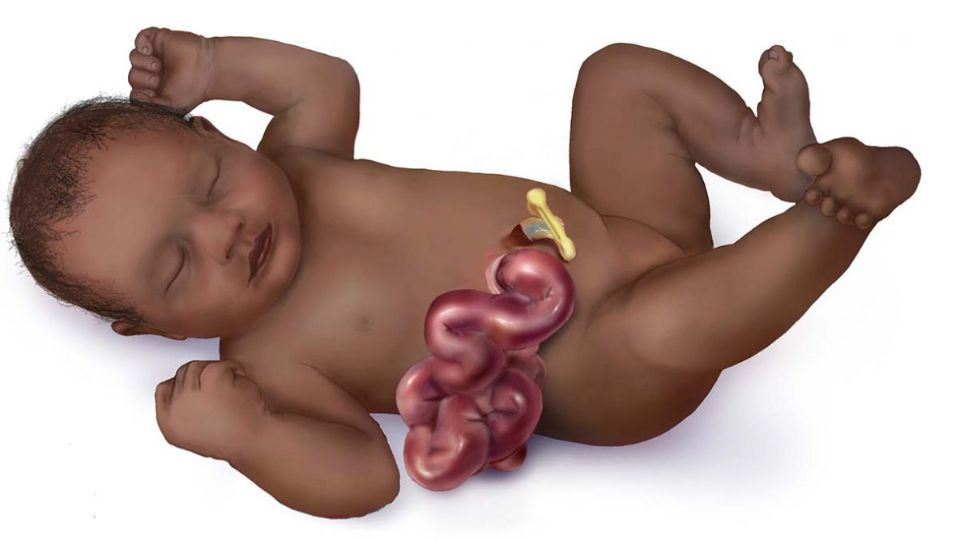
The Causes of Gastroshiza
The exact cause of gastroshiza remains unclear, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. There is no single factor that causes gastroshiza, but certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of the condition, including:
- Maternal Age: Mothers under 20 years old and over 40 years old are at higher risk of having a baby with gastroshiza.
- Maternal Smoking: Smoking during pregnancy has been linked to an increased risk of gastroshiza.
- Use of Certain Medications: Some medications taken during pregnancy may contribute to the development of gastroshiza.
- Genetic Factors: While gastroshiza is not typically inherited, some studies suggest that there may be a genetic component involved.
Symptoms of Gastroshiza
Gastroshiza is usually diagnosed during routine prenatal ultrasounds, typically between 18 and 20 weeks of pregnancy. The most obvious symptom of gastroshiza is the visible protrusion of the baby’s intestines from the abdominal cavity. In severe cases, the intestines may be partially or fully outside the body, and the baby may be born with exposed, unprotected intestines. Other potential symptoms or complications may include:
Also Read: Tribupneu: The Future of Efficient and Long-lasting Machinery
- Intestinal Malrotation: In some cases, the intestines may be improperly arranged in the abdominal cavity.
- Short Bowel Syndrome: This occurs if a significant portion of the intestines is missing or damaged, potentially leading to malnutrition.
- Infection Risk: The exposed intestines are vulnerable to infections, requiring immediate medical care.
- Delayed Growth: Babies born with gastroshiza may have difficulty gaining weight or growing as expected.
Diagnosing Gastroshiza
Gastroshiza is typically diagnosed through a prenatal ultrasound, where the protrusion of the intestines is clearly visible. This diagnosis is often made after the 18th week of pregnancy, during routine scans. Further imaging, such as a 3D ultrasound or MRI, may be used to assess the condition more thoroughly.
After birth, a physical examination of the newborn will confirm the diagnosis. A thorough evaluation of the extent of the defect will help guide treatment decisions. In some cases, additional imaging may be required to check for any other abnormalities in the digestive tract or surrounding organs.
Treatment Options for Gastroshiza
The treatment for gastroshiza depends on the severity of the condition, the extent of intestinal damage, and the overall health of the newborn. In most cases, surgical intervention is required shortly after birth to repair the defect and return the intestines to the abdominal cavity.
Also Read: Oncepik: Revolutionizing Digital Collaboration and Project Management
Surgical Repair
The primary treatment for gastroshiza is surgery, which involves placing the exposed intestines back into the abdominal cavity and closing the abdominal wall. The timing of the surgery depends on the health of the newborn and the extent of the defect, but it is typically performed within the first few days or weeks of life.
The surgeon may use a technique known as a “silo” or “silo bag,” which is a special pouch used to gradually return the intestines to the abdomen. This process can take several days or weeks, as the intestines are slowly pushed back into the body to allow the abdominal wall to close properly. Once the intestines are inside, the surgeon will close the hole in the abdominal wall, and the baby can begin recovering.
Post-Surgery Care
After surgery, the baby will require intensive care to monitor for any complications. This may include:
- Ventilator support: Some babies may need assistance with breathing, particularly if the lungs are underdeveloped.
- Nutritional support: Babies with gastroshiza may struggle with feeding initially, so they may need to be fed through a tube or IV while their intestines heal.
- Antibiotics: To prevent infections, antibiotics are commonly administered.
- Monitoring for Complications: The baby’s progress will be closely monitored to ensure there are no issues with bowel function, infection, or other complications.
Long-Term Outlook and Prognosis
The long-term prognosis for children born with gastroshiza has improved significantly over the years due to advances in surgical techniques and neonatal care. Most children who undergo surgery successfully can lead healthy lives, but there are potential long-term complications that parents should be aware of:
- Short Bowel Syndrome: If a significant portion of the intestines was damaged or missing, the child may have difficulty absorbing nutrients, leading to growth and developmental delays.
- Increased Risk of Infections: Children with gastroshiza may be at higher risk for infections, particularly in the early years as their immune systems develop.
- Digestive Issues: Some children may experience long-term digestive issues, such as constipation, reflux, or malabsorption, even after surgery.
Supporting Families Affected by Gastroshiza
Raising a child with gastroshiza can be emotionally and physically challenging for families. Support groups and resources are available to help parents navigate the complexities of their child’s diagnosis, treatment, and recovery. These groups provide valuable information, emotional support, and a community of families who understand the challenges.
Also Read: Oncepik: Revolutionizing Digital Collaboration and Project Management
Counseling and Support Services
Parents and caregivers of children with gastroshiza should consider seeking counseling and support services to help them cope with the emotional impact of the diagnosis. These services can provide essential coping strategies and offer resources for managing stress and anxiety.
FAQs about Gastroshiza
1. Can gastroshiza be prevented?
There is no guaranteed way to prevent gastroshiza, as it is primarily caused by genetic and environmental factors. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy, including not smoking and following prenatal care recommendations, may reduce the risk.
2. Is gastroshiza always fatal?
No, gastroshiza is not always fatal. With early diagnosis and appropriate surgical treatment, most children can survive and thrive. However, some may face ongoing health challenges related to short bowel syndrome or digestive issues.
3. How soon after birth is surgery required for gastroshiza?
Surgery is typically performed within the first few days of life, but the timing depends on the severity of the condition and the health of the newborn. Immediate surgical intervention is often required to prevent infections and complications.
4. What are the long-term effects of gastroshiza?
While many children with gastroshiza can live healthy lives, there may be long-term complications such as short bowel syndrome, feeding difficulties, and increased risk of infections. Regular follow-up care is essential for monitoring any potential issues.
5. Can gastroshiza recur in future pregnancies?
Gastroshiza is not generally considered hereditary, but the risk may be slightly higher in subsequent pregnancies, particularly if the mother had a previous child with the condition. Genetic counseling can provide more information about the risks.
Conclusion
Gastroshiza is a rare congenital condition that presents significant challenges for affected newborns and their families. However, with early diagnosis, surgical intervention, and comprehensive medical care, most children with gastroshiza can lead healthy lives. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and long-term outlook of gastroshiza is crucial for parents and healthcare providers alike. With the right support, children born with this condition can thrive and grow to lead fulfilling lives, despite the initial difficulties posed by gastroshiza.

